
This article aims to provide insights into the evolving sustainability implementation market, explaining the main challenges and opportunities.
It will enable you to not only understand what is happening and why, but also assess your sustainability maturity level.
We also provide key insights into the wining formula for engineering the next generation of sustainable businesses.

Elisa Gomez Gonzalez
Sustainability Strategist for Impact
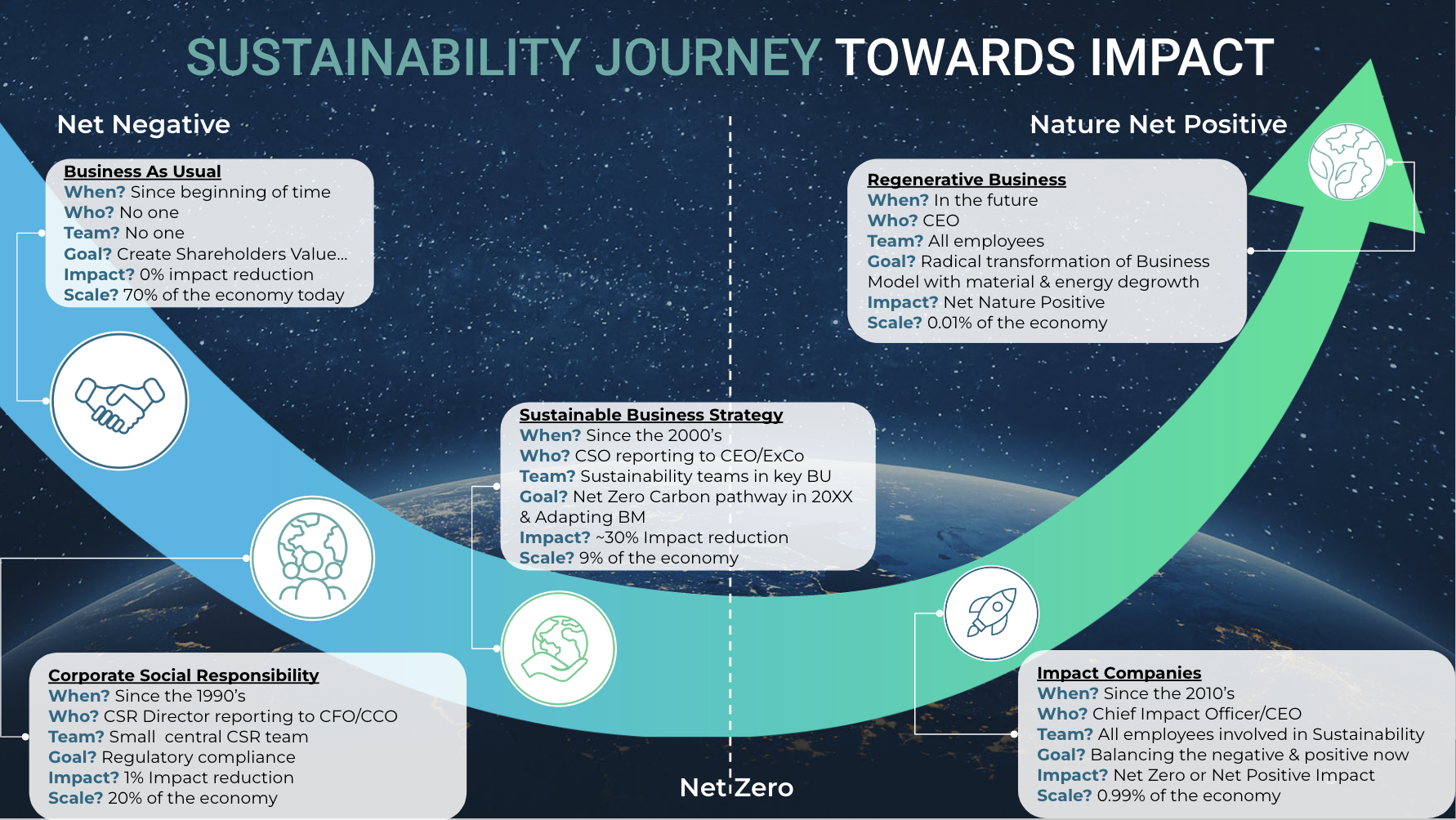
Sustainability Implementation & Market Growth: Challenges and Opportunities
In the last five years, all stakeholder groups have become more knowledgeable and demanding towards Sustainability management. What started with the triple bottom line and purely an ESG management approach directed towards Investors and Shareholders has shifted substantially towards value-driven science-based sustainability strategies.
We are currently in the shift from Business Strategy to Impact Companies. We like to call it Beyond Sustainability where companies work towards implementing value-driven science-based sustainability strategies that address both the footprint and the handprint.
Five main drivers triggering sustainability evolution:
How we got to this point is crucial in understanding the challenges and opportunities. The sudden rise and urgency that climate change and planetary boundaries have evidenced has triggered an exponential demand for qualified action. There is a pressing need to address change, and there have been five primary shifts that have triggered the ESG implementation urgency:
-
- Integration of financial and sustainability data
- Increasing regulations around ESG
- Pressure from stakeholders
- Higher exposure to risk and greenwashing accusations
- Rise of technology and digitalization within sustainability
1. Integration of Financial and sustainability data
Initially, ESG data disclosure was created to assess the rising risks of climate change, an effort driven by financial institutions and investors to gain valuable insights and rankings that could guide better decision-making on portfolio management. Even though ESG rating methodologies use vague methods for accounting for true sustainability impact, the market has increased dramatically; ESG data providers generated revenues above $1b in 2021, which could rise to $1.3b in 2022. Investor demand is a crucial driver of growth in the ESG data market, coupled with the rise of reporting on non-financial data, both mandatory and voluntary, where stakeholders want access to non-financial data such as customer satisfaction, employee engagement, social impact, environmental footprint, and innovation, which all provide additional insights and context to the financial analysis.
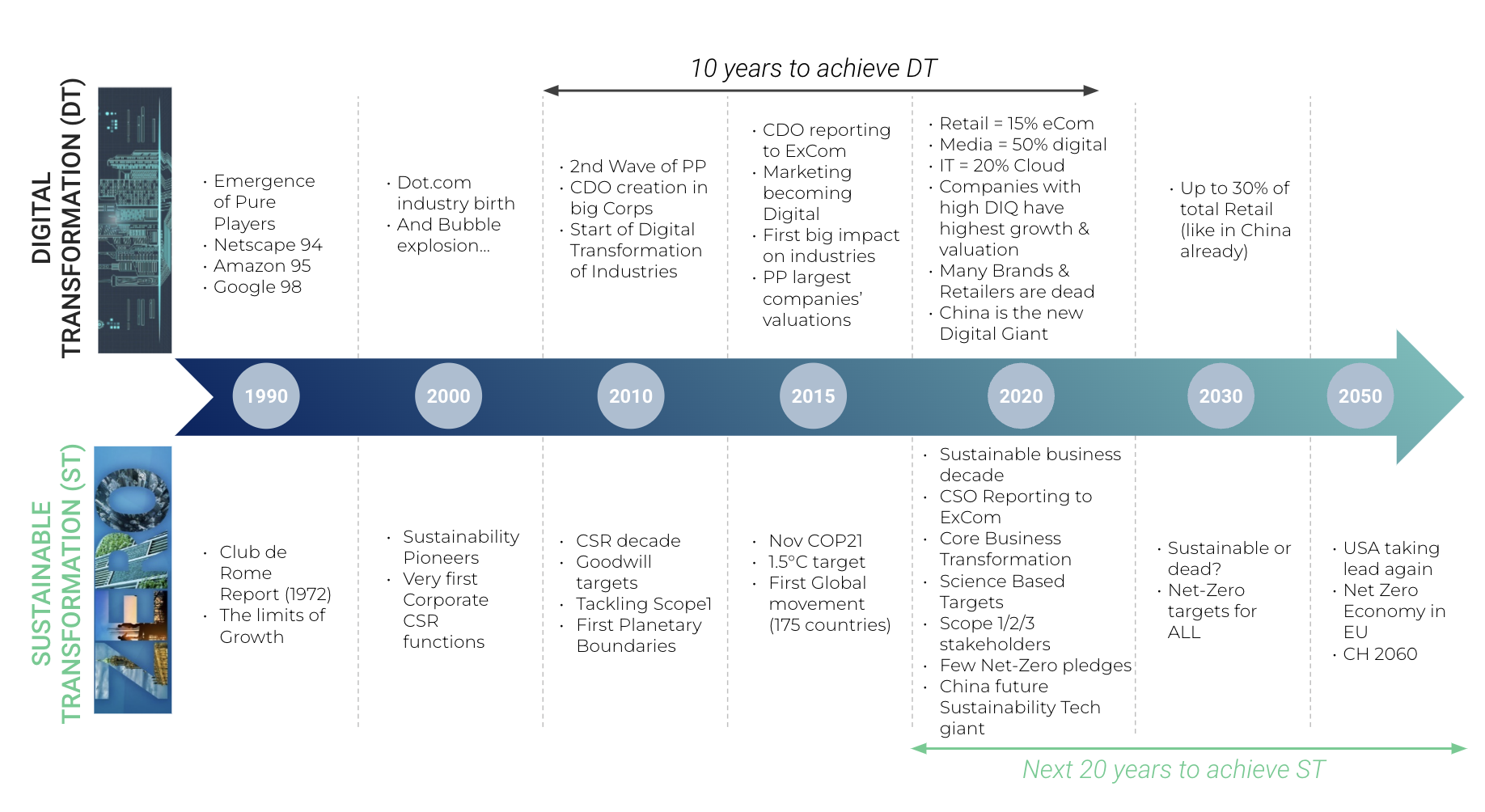
2. Increasing regulations and standards around sustainability (+ 180 new laws and norms)
Just in Europe, +180 of government legislation and norms on sustainability topics were announced by the end of 2022. Coupled with this, we have hundreds of Frameworks, Standards, Certifications, and Industry regulations emerging in various sustainability topics, addressing all sectors and the entire Value chain of operations. From Design to Use, there is regulation coming in for every aspect. The challenge lies in the substantial number of existing frameworks for sustainability implementation and reporting. As the diagram illustrates, there are so many options that it can be challenging to know which one to use or is more suitable for the company. So, if you need clarification on the diagram, we understand. The market needs a commonly accepted framework and methodology to measure sustainability/impact performance. The current level of complexity is overwhelming for all parties involved where extensive time is spent in gathering, reporting and consolidating information which doesn’t guide, support or trigger necessary improvements, mitigation actions or remediation processes.

3.Pressure from Stakeholders towards a Double materiality approach (outwards and inwards impacts)
A stakeholder may be affected by the project’s outcome, actively involved in the project’s work, or in a position to influence the project’s success. Customers, creditors, unions, and community members are external stakeholders, but stakeholders can also be internal members of a project’s organization, such as employees, suppliers, partners, and collaborators. Stakeholder engagement is a crucial pillar for sustainability implementation as Reporting is mainly directed and tailored towards the different groups of strategic stakeholders.
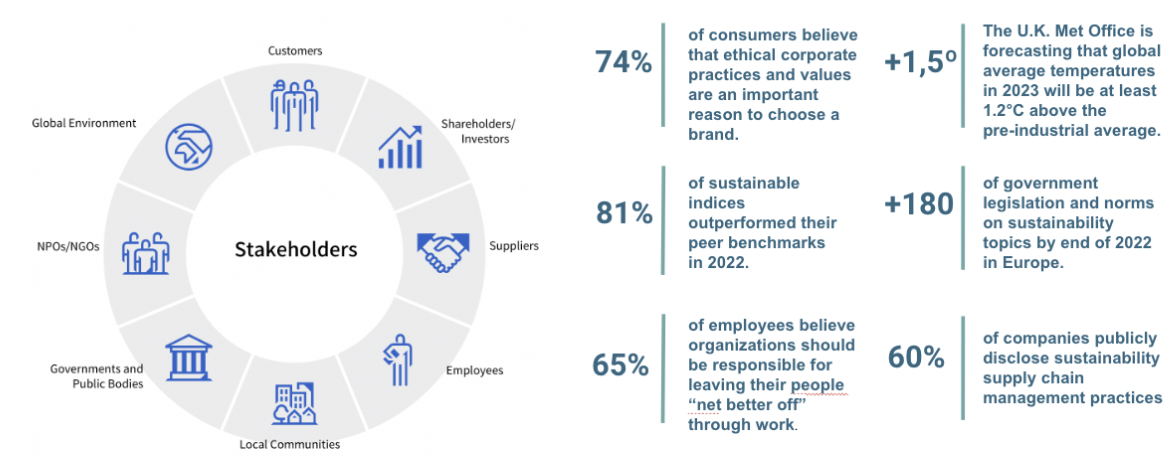
Traditionally, stakeholders are engaged to build Materiality Matrices where the company confronts its own importance topics to stakeholder, but the newly established concept of Double Materiality shed a whole new light into stakeholder engagement as more detailed information, perceptions and quantification is expected for each Material topic.
All stakeholder groups have seen, experienced, and demanded an increase in access to reliable and consistent sustainability data. Moreover, purpose has emerged as one key area where they expect a company to express publicly its commitment and what moves the company to operate in a specific way.
4.Higher exposure to risk and greenwashing accusations (companies need to walk the talk)
Companies have been developing a deeper understanding of the reputational issues that matter to their stakeholders and of the degree to which their products, services, operations, supply chains, and other activities affect those issues. Suppliers, Investments, and Clients are three key groups/operations where companies who claim high sustainability and impact within their offering should enforce/document the sustainability practices/outcomes of their operations in order to avoid reputation or greenwashing claims.
Carefully Screening, Selecting and Assessing suppliers in order to assure the same sustainability standards of the company through its supply chain
Carefully Selecting investments that are aligned with the company vision, values, purpose and sustainability
Carefully Selecting the Clients base in order to assure sustainability is achieved with the service/product provided but also that the company doesn’t contribute to causes that go against the companies sustainability principles.
5. Rise of Technology and Digitalization within Sustainability:
On the technology front, numerous companies are developing solutions to manage and report on sustainability data efficiently and effectively (from $905 million in 2021 to over $4.3 billion in 2027 at a 30% CAGR). Not only are new players emerging, but big corporations with decades of knowledge of foundational ESG are also developing their specific tech solutions, addressing the entire sustainability implementation process. Technology and digitalization ease the complexity of data, management, and reporting for all companies on a given topic or many. The sustainable transformation decade is booming, as is digital transformation.
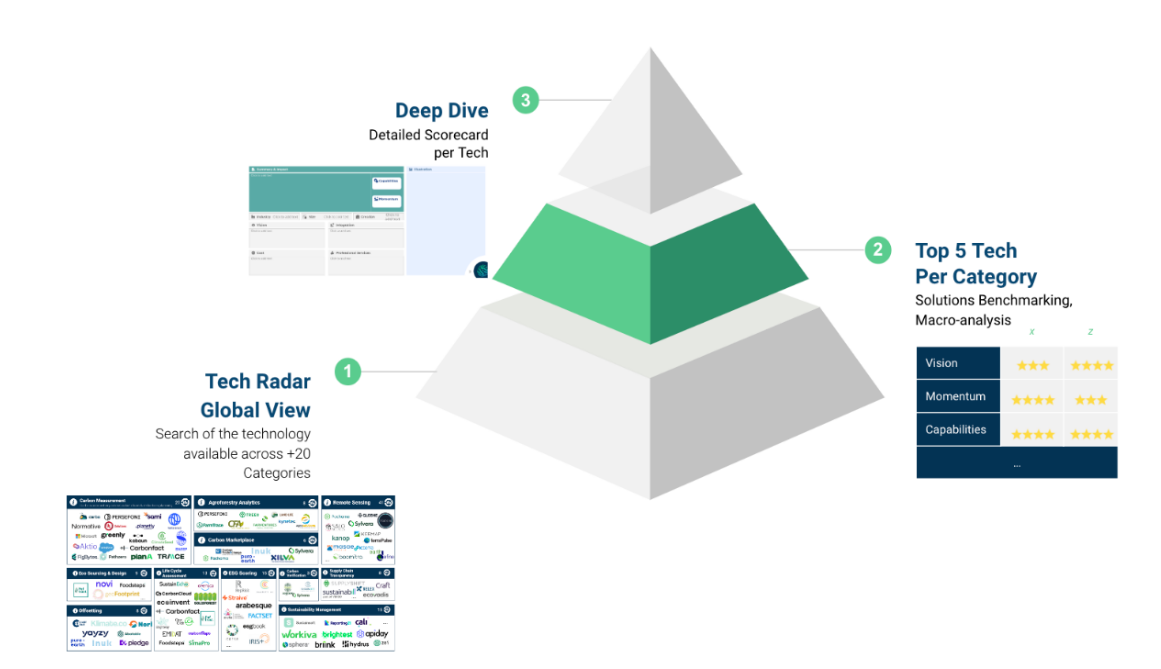
In order to navigate and leverage the complex technology set-up around sustainability implementation we have developed the Tech Radar and one Category focuses exclusively on sustainability management tools available for companies to ease their sustainability project management and process.
In order to navigate and leverage the complex technology set-up around sustainability implementation we have developed the Tech Radar and one Category focuses exclusively on sustainability management tools available for companies to ease their sustainability project management and process.
What is your level of sustainability Maturity?
Sustainable change can only be driven when the three value pillars of a sustainable business are aligned: Motivation, Accountability, and Ownership. That’s what we’re assessing with the Sustainability Maturity Path, a model created by PWC and adopted by us.
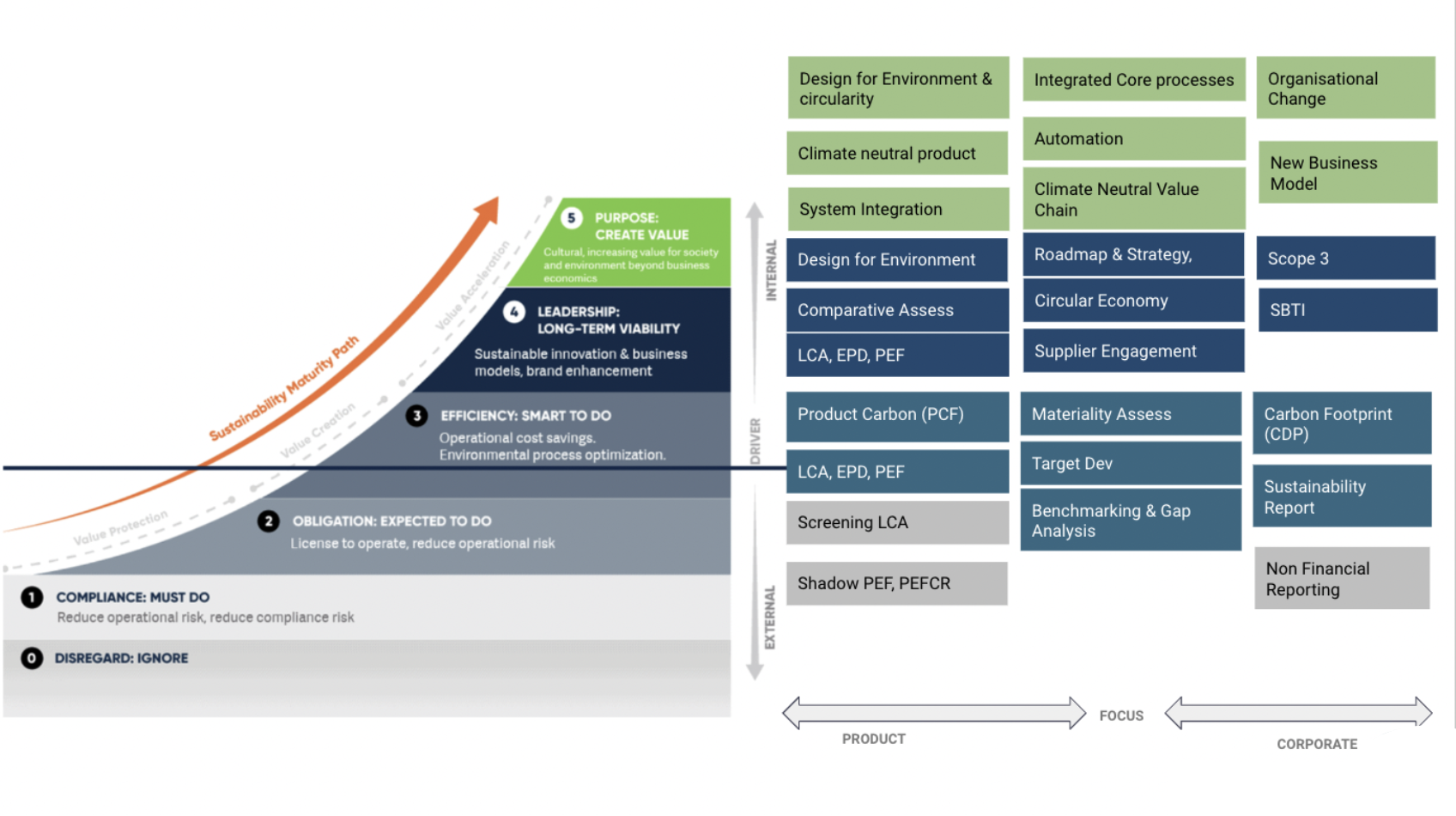
There are three main challenges to overcome for every organization, regardless of the level of maturity, when striving towards meaningful and impactful sustainability: weak relationships, poor data, and lack of authentic leadership.
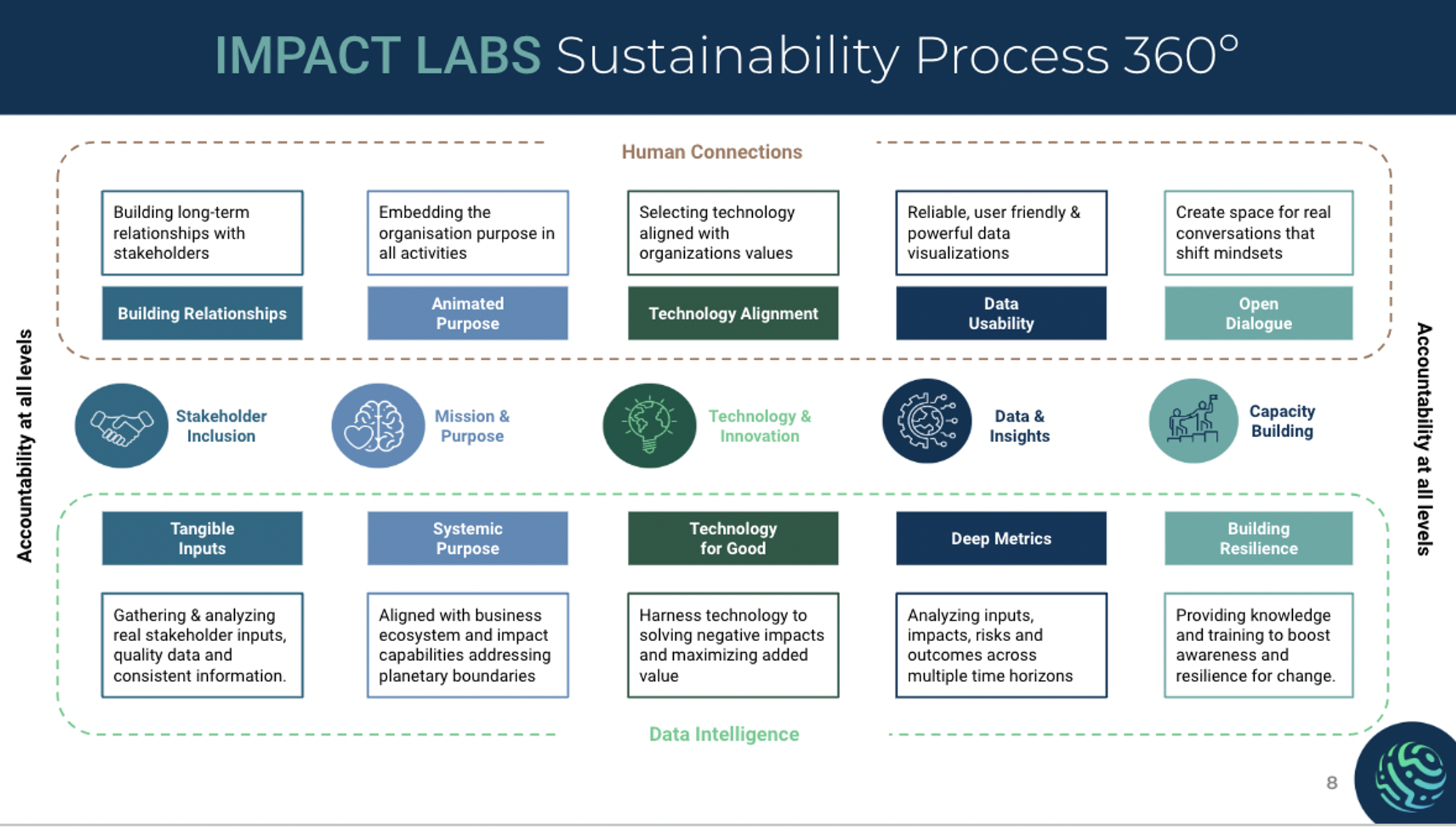
At Impact Labs, we aim to engineer the next generation of sustainable businesses because we are convinced we can shape a world where business is a force for good, driving positive impact on people, society, and the planet. We can help you with your sustainability journey and aim to highlight the following:
- Human Connections Approach to Stakeholder Relationships
- Data Intelligence
- Shared Ownership
Do not hesitate to contact us if you want to learn more on how we can help you accelerate your sustainable transformation
To learn more about our offer, visit our Consulting Solutions.
Listen to our podcast, Reboot Business, hosted by Julien Devaureix
Impact Labs CSRD Offer
We are happy to introduce our tailored CSRD service offer, designed to simplify compliance with the new regulations and drive impactful sustainability strategies. This way, teams can focus on reducing their footprint and developing effective nature strategies.
We streamline the CSRD reporting process with relevant tech and tools to make it as smooth and efficient as possible. Our service is designed to guide you through every step of this transformative journey.
Checklist on 10 key aspects to consider when selecting a CSRD Tool
Selecting the right technology for implementing the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) involves several key considerations to ensure compliance, efficiency, and effectiveness.
#REBOOT Business 12 – Une Economie Plus Juste
EPISODE SUMMARYAu fil des podcasts Reboot se dessine une ligne convergente vers l’urgence impérieuse de changer le système dans sa globalité. C’est...





